| Electrical Communication is a free textbook on the basics of communication technology. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Cables and Wave Guides Cables and Wave Guides  Loading Coils Loading Coils |
|||||





|
|||||
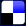
Loading CoilsCircuits not arranged for phantom service are loaded with coils17,18,19,20 such as those shown in Fig. 16. These consist of two windings separated by fiber washers represented
by the heavy black lines. The magnetic cores are continuous, although cores with air gaps have been used.11 Since the instantaneous currents in the two line wires are in opposite directions, the flux produced by each winding adds to that of the other, producing the maximum inductive effect.
The first loading coils had continuous ring-shaped cores consisting of a coil of many turns of fine iron wire. The wires were insulated to reduce eddy-current losses. In 1916 an important improvement was made when a core of powdered and compressed iron was perfected. A core of powdered and compressed Permalloy was developed17 about 1926. For about the same efficiency, the Permalloy core gives a coil very much smaller than the iron-core type, and hence it permits reductions in size. A further reduction in the size of loading coils is made practicable by the use of the molybdenum Permalloy dust core shown in Fig. 17. A detailed summary of recent improvements in cable loading coils and a description of the method of winding the coils is given in reference 20.
|
|||||
Home  Cables and Wave Guides Cables and Wave Guides  Loading Coils Loading Coils |
|||||
Last Update: 2011-05-18