| Electrical Communication is a free textbook on the basics of communication technology. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Telegraph Systems Telegraph Systems  The Differential Duplex System The Differential Duplex System |
|||





|
|||
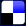
The Differential Duplex SystemA simplified differential duplex circuit operating on the double-current principle is shown in Fig. 11.
The two windings of the differential relays are identical. Thus; if the west station is sending and if the west artificial line exactly balances the impedance of the line and the entire east set, the current will divide equally through the two windings. The tendency of the two windings to produce magnetic attraction is then equal and opposite, and the sounder at the sending station is accordingly not operated. The current flowing over the line to the east station passes through the relay windings as indicated, causing the contacts to close, thus energizing the sounder circuit and producing an audible signal. Either distant sounder is therefore operated by current from the opposite station, and simultaneous two-way transmission is possible over one telegraph channel, which may be a grounded one-wire line. The differential duplex is widely used and is replacing the bridge duplex type.
|
|||
Home  Telegraph Systems Telegraph Systems  The Differential Duplex System The Differential Duplex System |
|||
Last Update: 2011-05-27