| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Real and Hyperreal Numbers Real and Hyperreal Numbers  Functions of Real Numbers Functions of Real Numbers  Absolute Value Function Absolute Value Function |
|






|
|
Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function is defined by a rule which is divided into two cases. DEFINITION The absolute value function | | is defined by
The absolute value of x gives the distance between x and 0. It is always positive or zero. For example, |3| = 3, |-3| = 3, |0|=0. The domain of the absolute value function is the whole real line R while its range is the interval [0, ∞). The absolute value function can also be described by the rule
Its graph is given by the equation y = 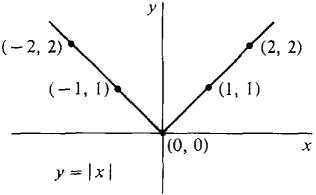 Figure 1.2.10 If a and b are two points on the real line, then from the definition of |x| we see that
Thus |a — b| is the difference between the larger and the smaller of the two numbers. In other words, |a - b| is the distance between the points a and b, as illustrated in Figure 1.2.11. 
Figure 1.2.11 For example, |2 - 5| = 3, |4 - ( -4)| = 8. Here are some useful facts about absolute values.
|
|
Home  Real and Hyperreal Numbers Real and Hyperreal Numbers  Functions of Real Numbers Functions of Real Numbers  Absolute Value Function Absolute Value Function |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-09




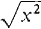 . The graph is the V shown in Figure 1.2.10.
. The graph is the V shown in Figure 1.2.10.