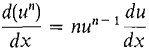| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Differentiation Differentiation  Derivatives of Rational Functions Derivatives of Rational Functions  Theorem 5: Power Rule Theorem 5: Power Rule  Principle of Induction Principle of Induction |
|






|
|
Principle of Induction
In the proof of the Power Rule, we used the following principle: PRINCIPLE OF INDUCTION Suppose a statement P(n) about an arbitrary integer n is true when n = 1. Suppose further that for any positive integer m such that P(m) is true, P(m + 1) is also true. Then the statement P(n) is true of every positive integer n. In the previous proof, P(n) was the Power Rule,
The Principle of Induction can be made plausible in the following way. Let a positive integer n be given. Set m = 1; since P(1) is true, P(2) is true. Now set m = 2; since P(2) is true, P(3) is true.. We continue reasoning in this way for n steps and conclude that P(n) is true. The Power Rule also holds for n = 0 because when u ≠ 0, u0 = 1 and d1/dx = 0. Using the Sum, Constant, and Power rules, we can compute the derivative of a polynomial function very easily. We have
and thus
|
|
Home  Differentiation Differentiation  Derivatives of Rational Functions Derivatives of Rational Functions  Theorem 5: Power Rule Theorem 5: Power Rule  Principle of Induction Principle of Induction |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-25