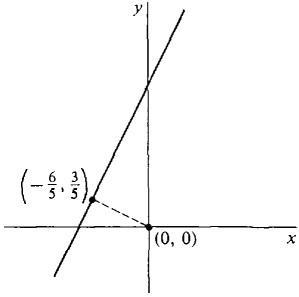| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Continuous Functions Continuous Functions  Maxima and Minima Maxima and Minima  Examples Examples  Example 4 Example 4 |
|||||||






|
|||||||
Example 4
Find the point on the line y = 2x + 3 which is at minimum distance from the origin. The distance is given by
and substituting 2x + 3 for y,
This is defined on the whole real line.
CONCLUSION The distance is a minimum at x = -(6/5), y = 2x + 3 = 3/5. The minimum distance is
This is shown in Figure 3.5.9.
Figure 3.5.9
|
|||||||
Home  Continuous Functions Continuous Functions  Maxima and Minima Maxima and Minima  Examples Examples  Example 4 Example 4 |
|||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-25


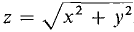

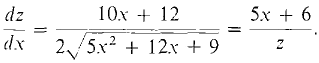
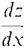 = 0
= 0 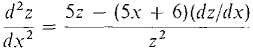
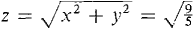 .
.