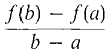| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Continuous Functions Continuous Functions  Properties of Continuous Functions Properties of Continuous Functions  Average Slope Between Two Points Average Slope Between Two Points |
|






|
|
Average Slope Between Two Points
Our method of sketching curves in Section 3.7 depends on a consequence of Rolle's Theorem called the Mean Value Theorem. It deals with the average slope of a curve between two points. DEFINITION Let f be defined on the closed interval [a, b]. The average slope of f between a and b is the quotient average slope = We can see in Figure 3.8.17 that the average slope of f between a and b is equal to the slope of the line passing through the points (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)). This is shown by the two-point equation for a line (Section 1.3). In particular, if f is already a linear function f(x) = mx + c, then the average slope of f between a and b is equal to the slope m of the line y =f(x).
Figure 3.8.17 Average Slope This is shown by the two-point equation for a straight line (Section 1.2). In particular, if f is already a linear function f(x) = mx + c, then the average slope of f between a and b is equal to the slope m of the straight line y = f(x).
|
|
Home  Continuous Functions Continuous Functions  Properties of Continuous Functions Properties of Continuous Functions  Average Slope Between Two Points Average Slope Between Two Points |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-05