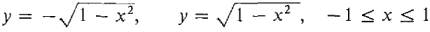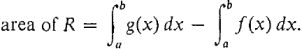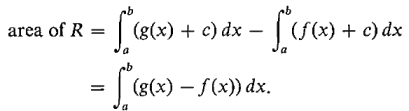| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Integral Integral  Area between two Curves Area between two Curves  Area between two Curves Area between two Curves |
|||||||






|
|||||||
Area between two Curves
Figure 4.5.1 A region in the plane can often be represented as the region between two curves. For example, the unit circle is the region between the curves
shown in Figure 4.5.1. Consider two continuous functions f and g on [a, b] such that f (x) ≤ g(x) for all x in [a, b]. The region R, bounded by the curves y = F(x), y = g(x), x = a, x = b, is called the region between f (x) and g(x) from a to b. If both curves are above the x-axis as in Figure 4.5.2, the area of the region R can be found by subtracting the area below f from the area below g:
It is usually easier to work with a single integral and write
Figure 4.5.2 In the general case shown in Figure 4.5.3, we may move the region R above the x-axis by adding a constant c to both f(x) and g(x) without changing the area, and the same formula holds:
Figure 4.5.3 To sum up, we define the area between two curves as follows. DEFINITION If f and g are continuous and f (x) ≤ g(x) for a ≤ x ≤ b, then the area of the region R between f(x) and g(x) from a to b is defined as
|
|||||||
Home  Integral Integral  Area between two Curves Area between two Curves  Area between two Curves Area between two Curves |
|||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-25