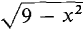| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Applications of the Integral Applications of the Integral  Infinite Sum Theorem Infinite Sum Theorem  Examples Examples  Example 2: Cylindrical Wedge Example 2: Cylindrical Wedge |
|






|
|
Example 2: Cylindrical Wedge
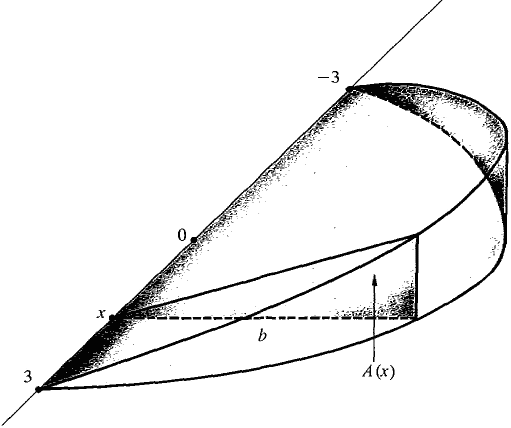
A wedge is cut from a cylindrical tree trunk of radius 3 ft, by cutting the tree with two planes meeting on a line through the axis of the cylinder. The wedge is 1 ft thick at its thickest point. Find its volume.
Figure 6.1.8 Example 2 The wedge is shown in Figure 6.1.8. The cross sections perpendicular to the x-axis are similar triangles. Place the edge along the x-axis with x from - 3 to 3. At the thickest point, where x = 0, the cross section is a triangle with base 3 ft and altitude 1 ft. The base of the cross section triangle at x is b = and the altitude is ⅓b = ⅓ The area of the cross section is A(x) = ½ · base · altitude = ½b · ⅓b = 1/6b2 = 1/6(9 - x2). The volume is thus
The solution is 6 cubic feet.
|
|
Home  Applications of the Integral Applications of the Integral  Infinite Sum Theorem Infinite Sum Theorem  Examples Examples  Example 2: Cylindrical Wedge Example 2: Cylindrical Wedge |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-22