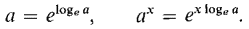| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Exponential and Logartihmic Functions Exponential and Logartihmic Functions  Derivatives of Exponential Functions and the Number e Derivatives of Exponential Functions and the Number e  Examples Examples  Example 3 Example 3 |
||||||||||






|
||||||||||
Example 3
Find d(ax)/dx. We use the formula
Put u = x loge a. Then ax = ea, so
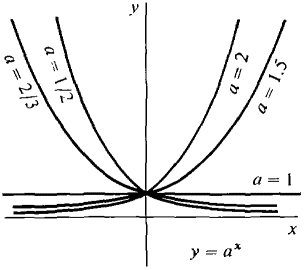
This example shows that the derivative of ax is equal to the constant loge a times ax itself. Figure 8.3.3 shows the graph of y = ax for various values of a > 0.
Figure 8.3.3
The slope of the curve y = ax at x = 0 is always equal to loge a. For all values of a > 0, ax is positive for all x, so the derivative has the same sign as logea. The three possibilities are shown:
|
||||||||||
Home  Exponential and Logartihmic Functions Exponential and Logartihmic Functions  Derivatives of Exponential Functions and the Number e Derivatives of Exponential Functions and the Number e  Examples Examples  Example 3 Example 3 |
||||||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-15