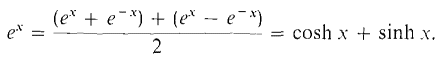| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Exponential and Logartihmic Functions Exponential and Logartihmic Functions  Some Differential Equations Some Differential Equations  Examples Examples  Example 5 Example 5 |
|






|
|
Example 5
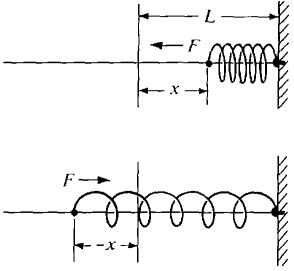
When a spring of natural length L is compressed a distance x it exerts a force F = -kx. The negative sign indicates that the force is in the opposite direction from x (Figure 8.6.3).
Figure 8.6.3 When x is negative the spring is expanded and the equation F = -kx still holds. Suppose a mass m is attached to the end of the spring and at time t = 0 is at position x0 and has velocity v0. The motion of the mass follows the differential equation
The general solution is x = a cos cot + b sin ωt where
This function is periodic with period 2π/ω, so as expected the mass oscillates back and forth. In the following second order equation, hyperbolic sines and cosines arise. The general solution of the differential equation d2y/dx2 = y is y = a cosh x + b sinh x. We see that cosh x and sinh x are solutions because
Another solution is ex. Note that
|
|
Home  Exponential and Logartihmic Functions Exponential and Logartihmic Functions  Some Differential Equations Some Differential Equations  Examples Examples  Example 5 Example 5 |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-16


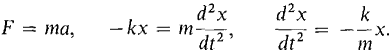
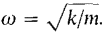 Using the initial conditions, the motion of the mass is
Using the initial conditions, the motion of the mass is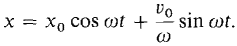
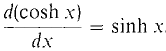 ,
, 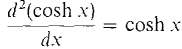 ,
,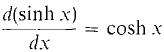 ,
, 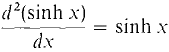 .
.