| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Partial Differentiation Partial Differentiation  Maxima and Minima Maxima and Minima  Examples Examples  Example 1: Closed Rectangle Example 1: Closed Rectangle |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Example 1: Closed Rectangle
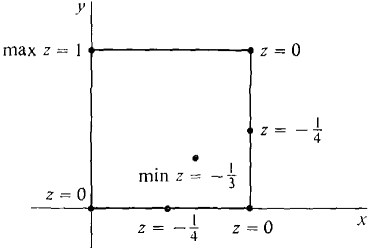
Find the maximum and minimum of z = x2 + y2 - xy - x on the closed rectangle 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0 ≤ y ≤ 1.
The values from Steps 3 and 4 are also shown on the sketch of D in Figure 11.7.5.
Figure 11.7.5 CONCLUSION Maximum: z = 1 at (0, 1) Minimum: z = -⅓ at(⅔, ⅓). The maximum is at a boundary point and the minimum at an interior point.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Home  Partial Differentiation Partial Differentiation  Maxima and Minima Maxima and Minima  Examples Examples  Example 1: Closed Rectangle Example 1: Closed Rectangle |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-15


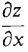 = 2x - y - 1,
= 2x - y - 1, 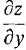 = 2y - x.
= 2y - x.