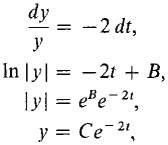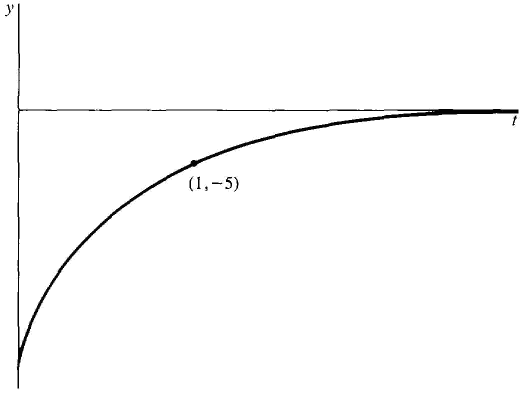| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Differential Equations Differential Equations  Equations with Seperable Variables Equations with Seperable Variables  Examples Examples  Solve the Initial Value Problem Solve the Initial Value Problem |
|||||||||






|
|||||||||
Solve the Initial Value Problem
Figure 14.1.4 Example 1
|
|||||||||
Home  Differential Equations Differential Equations  Equations with Seperable Variables Equations with Seperable Variables  Examples Examples  Solve the Initial Value Problem Solve the Initial Value Problem |
|||||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-17