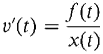| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |
|

Home  Differential Equations Differential Equations  First Order Linear Equations First Order Linear Equations  Solving A First Order Linear Differential Equation Solving A First Order Linear Differential Equation |
|||||||||||||||






|
|||||||||||||||
Solving A First Order Linear Differential Equation
(1) y'+ p(t)y = f(t). The corresponding homogeneous linear differential equation is (2) x' + p(t)x = 0.
Discussion Step 2 gives us a function v(t) for which v'(t)x(t) = f(t). Therefore, by our previous discussion, v(t)x(t) is a particular solution of the linear equation (1). Step 3 is then justified by Theorem 1.
|
|||||||||||||||
Home  Differential Equations Differential Equations  First Order Linear Equations First Order Linear Equations  Solving A First Order Linear Differential Equation Solving A First Order Linear Differential Equation |
|||||||||||||||
Last Update: 2006-11-17