| VIAS Encyclopedia provides a collection of tables and definitions commonly needed in science and engineering. |

|

Home  Chemistry Chemistry  Organic Compounds Organic Compounds  Theobromine Theobromine |
|






|
|
Theobromine
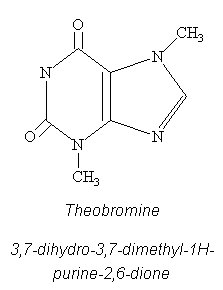
Theobromine is a bitter alkaloid of the methylxanthine family, which also includes the similar compounds theophylline and caffeine. It is known to induce mutations in bacteria and lower eukaryotes, but does not seem to cause mutations in higher eukaryotes, such as humans. Theobromine is a chemical stimulant frequently confused with caffeine, but has very different effects on the human body. It is a mild, lasting stimulant with a mood improving effect. In medicine, it is used as a diuretic, vasodilator, and myocardial stimulant. Theobromine is the primary alkaloid found in cocoa and chocolate (Theobroma cacao is the scientific name of the cacao tree). Its presence is one of the causes for chocolate's mood-elevating effects. In chocolate, theobromine exists in doses that are safe for humans to consume in large quantities, but can be lethal for animals such as dogs and horses, as they metabolize theobromine more slowly. Scientists have recently discovered that theobromine has an antitussive effect superior to codeine by suppressing vagus nerve activity. Alternate names are: Riddospas, Riddovydrin, Santheose, Seominal, Theobrominum, Theoguardenal, Theominal and Théoxalvose.
|
|
Home  Chemistry Chemistry  Organic Compounds Organic Compounds  Theobromine Theobromine |
|
Last Update: 2005-05-30

