| The Java Course provides a general introduction to programming in Java. It is based on A.B. Downey's book, How to Think Like a Computer Scientist. Click here for details. |

|

Home  Arrays Arrays  Copying Arrays Copying Arrays |
||






|
||
Copying Arrays
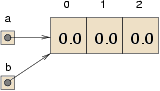
When you copy an array variable, remember that you are copying a reference to the array. For example: double[] b = a; This code creates one array of three doubles, and sets two different variables to refer to it. This situation is a form of aliasing.
Any changes in either array will be reflected in the other. This is not usually the behavior you want; instead, you should make a copy of the array, by allocating a new array and copying each element from one to the other. double[] b = new double [3];int i = 0; while (i < 4) { b[i] = a[i]; i++; }
|
||
Home  Arrays Arrays  Copying Arrays Copying Arrays |
||
Last Update: 2011-01-24