| Electrical Communication is a free textbook on the basics of communication technology. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Telephone Exchange Service and Systems Telephone Exchange Service and Systems  Sidetone Circuits Sidetone Circuits |
|||





|
|||
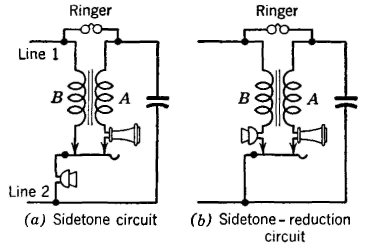
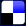
Sidetone CircuitsA typical common-battery sidetone circuit is shown in Fig. 7(a). The transmitter receives direct current from the battery in the central office over the two line wires. When sound waves strike the transmitter diaphragm, the current is caused to vary in accordance with these sound waves (Fig. 4). The alternating voltage generated at the transmitter will force a current through the series path consisting of the receiver, winding A of the induction coil, and the capacitor. In a typical telephone set, this capacitor neutralizes, to some extent (depending on the frequency), the inductive reactance of the receiver, thus lowering the impedance and increasing the current flow in the receiver circuit. This current produces side-tone as previously mentioned. In addition, this current induces an electromotive force in the winding B of the induction coil (which has an unequal ratio of turns and thus acts as a step-up transformer), and this induced voltage adds to the alternating voltage produced at the transmitter terminals, hence increasing the total voltage impressed on the line. With the sidetone-reduction circuit of Fig. 7(b), the direct current received by the transmitter is about the same as in the sidetone circuit, and thus the alternating voltage output corresponding to the impinging sound waves is about the same. This voltage causes a current to flow through winding B of the induction coil, and this current induces a voltage in winding A. Since the induction coil now acts as a step-down transformer, the induced voltage in A is considerably less than the voltage impressed across the receiver circuit in the sidetone set. A smaller current flows through the receiver under these conditions, and less sidetone is produced. The receiving efficiency is increased but the sidetone-reduction circuit does not impress so high a voltage on the line as the sidetone circuit and is less efficient in transmitting.
|
|||
Home  Telephone Exchange Service and Systems Telephone Exchange Service and Systems  Sidetone Circuits Sidetone Circuits |
|||
Last Update: 2011-05-03