| Electrical Communication is a free textbook on the basics of communication technology. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Interference and Noise Interference and Noise  Classification of Power Parallels Classification of Power Parallels |
|||





|
|||
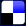
Classification of Power ParallelsFrom the standpoint of inductive interference there are many possible types of power parallels. The arrangement of the conductors or configuration greatly affects the induction.18 In the following pages, the discussion will be limited to three-phase circuits having triangular configuration. These circuits may be classified as follows: (1) non-transposed, non-grounded; (2) non-transposed, grounded; (3) transposed, non-grounded; and (4) transposed, grounded. Power lines, when grounded, are usually grounded at the neutrals of three-phase, wye-connected transformer banks. The neutrals of alternators are often grounded. There are in general three types of grounds in common use in this country: first, a direct connection to earth; second, grounds through current-limiting resistors or reactors; and third, grounds through parallel-resonant circuits offering low impedance to the fundamental, but greatly attenuating noise-producing harmonics. The influence factor varies greatly with grounding arrangements. Although there are other reasons why it is desirable to ground neutrals, one is that it offers a protection to equipment in the event of a ground on one of the line wires, and thus insulation costs are less. This is shown in Fig. 13. The transformer or alternator windings must be insulated from the core which is assumed to be at ground potential. If the windings are not grounded and an accidental ground occurs on wire 3? the voltages between windings and core at points 1 and 2 will now be approximately 1.73Ew, where Ew is the voltage in each winding. If, however, a ground is in existence at the neutral of the winding as shown dotted and if then an accidental ground occurs on wire 3, the voltage at points 1 and 2 cannot rise above Ew.
|
|||
Home  Interference and Noise Interference and Noise  Classification of Power Parallels Classification of Power Parallels |
|||
Last Update: 2011-05-30