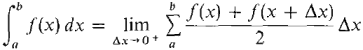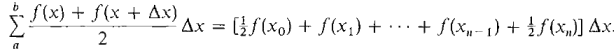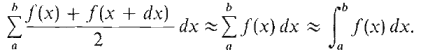| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Integral Integral  Numerical Integration Numerical Integration  Trapezoidal Approximation Trapezoidal Approximation |
|






|
|
Trapezoidal Approximation
We thus make the definition: DEFINITION Let Δx = (b - a)/n evenly divide b - a. Then by the trapezoidal approximation to the definite integral
The Trapezoidal Approximation of an integral ½f(x0) + f(x1) + f(x2) + ... + ½ f(xn) by cumulative addition. Then multiply this sum by Δx to obtain the Trapezoidal Approximation. THEOREM 1 For a continuous junction f on [a, b], the trapezoidal approximation approaches the definite integral as Δx → 0+, that is,
PROOF Comparing the formulas for the trapezoidal approximation and the Riemann sum, we see that
For dx positive infinitesimal, the extra term (½f(xH)-½f(x0))dx is infinitely small. It follows that
|
|
Home  Integral Integral  Numerical Integration Numerical Integration  Trapezoidal Approximation Trapezoidal Approximation |
|
Last Update: 2010-11-26


 we mean the sum
we mean the sum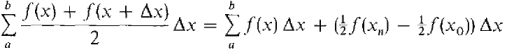
 can be computed very efficiently on most hand calculators. First compute the sum
can be computed very efficiently on most hand calculators. First compute the sum