| Transistor Basics is a free introductory textbook on transistors and their basic applications. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Transistor Amplifiers Transistor Amplifiers  The D-C Operating Point The D-C Operating Point  Fixed Bias Fixed Bias |
||






|
||
|
Fixed BiasAuthor: Leonard Krugman
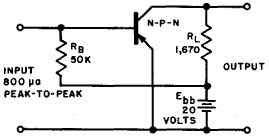
Fig. 5-2. Fixed-bias operation.
 ohms. ohms.
This value includes the emitter to base resistance, but since re + rb is generally only a few hundred ohms, they can be neglected. The resulting circuit, with the calculated values, is illustrated in Fig. 5-2 for a N-P-N transistor. If the same characteristics were applied to a P-N-P type, the only circuit change would be a reversal of the supply battery potentials. The transistor bias indicated in this figure is called fixed bias,
|
||
Home  Transistor Amplifiers Transistor Amplifiers  The D-C Operating Point The D-C Operating Point  Fixed Bias Fixed Bias |
||
Last Update: 2010-11-17