| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Applications of the Integral Applications of the Integral  Improper Integrals Improper Integrals  Problems Problems |
|






|
|
Problems
In Problems 1-36, test the improper integral for convergence and evaluate when possible.
37 Show that if r is a rational number, the improper integral 38 Show that if r is rational, the improper integral 39 Find the area of the region under the curve y = 4x-2 from x = 1 to x = x. 40 Find the area of the region under the curve 41 Find the area of the region between the curves y = x-1/4 and y = x-1/2 from x = 0 to x = 1. 42 Find the area of the region between the curves y = -x-3 and y = x-2, 1 ≤ x < x. 43 Find the volume of the solid generated by rotating the curve y = l/x, 1 ≤ x < x, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis. 44 Find the volume of the solid generated by rotating the curve y = x-1/3, 0 < x ≤ 1, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis. 45 Find the volume of the solid generated by rotating the curve y = x-3/2, 0 < v ≤ 4, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis. 46 Find the volume generated by rotating the curve y = 4x-3, -∞ < ∞ ≤ -2, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis. 47 Find the length of the curve 48 Find the length of the curve y = ¾x1/3 - 3/5 x5/3 from x = 0 to x = 1. 49 Find the surface area generated when the curve y = √x - ⅓x√x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, is rotated about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis. 50 Do the same for the curve y = ¾x1/3 - 3/5 x5/3,0 ≤ x ≤ 1. 51 (a) Find the surface area generated by rotating the curve y = √x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, about the x-axis. (b) Set up an integral for the area generated about the y-axis. 52 Find the surface area generated by rotating the curve y = x2/3, 0 ≤ x ≤ 8, about the x-axis. 53 Find the surface area generated by rotating the curve 54 The force of gravity between particles of mass m1 and m2 is F = gm1m2/s2 where s is the distance between them. If m1 is held fixed at the origin, find the work done in moving m2 from the point (1,0) all the way out the x-axis. H 55 Show that the Rectangle and Addition Properties hold for improper integrals.
|
|
Home  Applications of the Integral Applications of the Integral  Improper Integrals Improper Integrals  Problems Problems |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-25



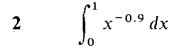
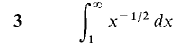
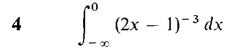

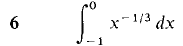
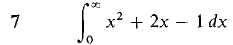
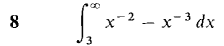
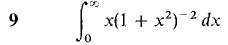

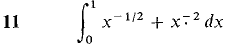
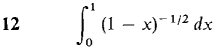





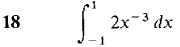



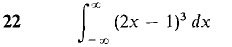

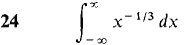

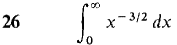



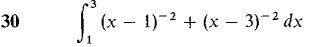



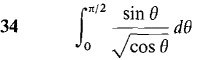
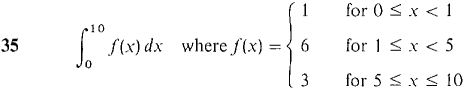

 converges when r < 1 and diverges when r > 1.
converges when r < 1 and diverges when r > 1.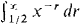 converges when r > 1 and diverges when r < 1.
converges when r > 1 and diverges when r < 1. from x = ½ to x = 1.
from x = ½ to x = 1.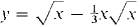 from x = 0 to x = 1.
from x = 0 to x = 1. , 0 ≤ x ≤ a, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis (0 < a ≤ r).
, 0 ≤ x ≤ a, about (a) the x-axis, (b) the y-axis (0 < a ≤ r).