| The ebook Elementary Calculus is based on material originally written by H.J. Keisler. For more information please read the copyright pages. |

|

Home  Infinite Series Infinite Series  Power series Power series  Theorem 1: Convergence and Divergence Theorem 1: Convergence and Divergence |
|






|
|
Theorem 1: Convergence and Divergence
THEOREM 1 (i) If a power series
converges when x = u, then it converges absolutely whenever |x| < |u|. (ii) If a power series diverges when x = v, then it diverges whenever |x| > |v|. PROOF (i) Suppose the series
(ii) This follows trivially from (i).
Theorem 1 shows that if a power series converges at x = u and at x = v, then it converges absolutely at every point strictly between u and v. We conclude that the set of points where the power series converges is an interval, called the interval of convergence. (A rigorous proof that the set is an interval is given in the Epilogue.) The next corollary summarizes what we know about the interval of convergence. COROLLARY For each power series (i) The series converges absolutely at x = 0 and diverges everywhere else. (ii) The series converges absolutely on the whole real line (-∞, ∞). (iii) The series converges absolutely at every point in an open interval (-r, r) and diverges at every point outside the closed interval [-r, r]. At the endpoints -r and r the series may converge or diverge, so the interval of convergence is one of the sets (-r,r), [-r, r), (-r, r], [-r, r]. Figure 9.7.1 illustrates part (iii) of the Corollary. The number r is called the radius of convergence of the power series. In case (i) the radius of convergence is zero, and in case (ii) it is ∞. Once the radius of convergence is determined, we need only test the series at x = r and x = -r to find the interval of convergence.
Figure 9.7.1
|
|
Home  Infinite Series Infinite Series  Power series Power series  Theorem 1: Convergence and Divergence Theorem 1: Convergence and Divergence |
|
Last Update: 2006-11-08



 converges.
converges. 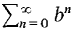 converges,
converges,
 converges absolutely,
converges absolutely, diverge and |u| > |v|.
diverge and |u| > |v|.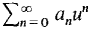 cannot converge because if it did
cannot converge because if it did  would convergeabsolutely. Therefore
would convergeabsolutely. Therefore 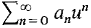 diverges.
diverges. , one of the following happens.
, one of the following happens.