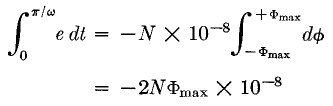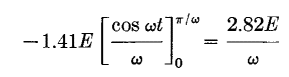| Electronic Transformers and Circuits is a free introductory textbook on transformers and related circuits. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Introduction Introduction  Flux and Average Voltage Flux and Average Voltage |
|||||||||






|
|||||||||
Flux and Average Voltage
an expression for flux may be found :
Now if we consider the time interval 0 to π/ω, we have
Equation 9 gives the relation between maximum flux and the time integral of voltage. The left side of the equation is the area under the voltage-time wave. For a given frequency, it is proportional to the average voltage value. This is perfectly general and holds true regardless of wave form. If the voltage wave form is alternating, the average value of the time integral over a long period of time is zero. If the voltage wave form is sinusoidal, the flux wave form is also sinusoidal but is displaced 90° as in Fig. 5, and the integral over a half-cycle is
whence
Equation 10 is the relation between maximum flux, effective voltage, frequency, and turns. It is a transposed form of equation 4.
|
|||||||||
Home  Introduction Introduction  Flux and Average Voltage Flux and Average Voltage |
|||||||||
Last Update: 2011-01-24