You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information. You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information.
|
|
Transposed Matrix
| Transposed Matrix |
The transpose of a given matrix M of order m n is
the matrix MT, which is
obtained by exchanging the order of the indices: (mrs
)T = (msr ). This new
matrix MT is of the order
n n is
the matrix MT, which is
obtained by exchanging the order of the indices: (mrs
)T = (msr ). This new
matrix MT is of the order
n m. m. |
More simply expressed, we just write the rows as columns, and vice versa.
Here is an example:
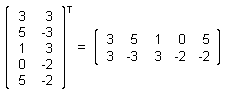
It is evident that MTT equals M, where
MTT is the
transpose of the transpose of M.
| Symmetric Matrix |
The matrix M is called symmetric if M
= MT. |
| Skew-Symmetric Matrix |
If M = -MT, the matrix is called skew-symmetric or
anti-symmetric. |
Last Update: 2005-Jšn-25
 You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information.
You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information.
 You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information.
You are working with the text-only light edition of "H.Lohninger: Teach/Me Data Analysis, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-New York-Tokyo, 1999. ISBN 3-540-14743-8". Click here for further information.
 Math Background
Math Background  Matrices
Matrices  Transposed Matrix
Transposed Matrix