| Transistor Basics is a free introductory textbook on transistors and their basic applications. See the editorial for more information.... |

|

Home  Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors  The Grounded Collector Connection The Grounded Collector Connection  Voltage Gain Voltage Gain |
|






|
|
|
Voltage Gain in the Grounded Collector ConnectionAuthor: Leonard Krugman The voltage gain, as defined in equation 3-24 by the general four-terminal parameters is:
Under the conditions for infinite input resistance and infinite current gain (RL = -r22), the voltage gain becomes:
For a perfect buffer stage Rc + rc- rm = 0. Thus, the voltage gain equation becomes
The maximum voltage gain as defined by equation 3-25 is
this becomes. For the typical point-contact transistor, when RL = 15,000 ohms
Under the conditions RL = -r22 = 11,850 ohms VG = Under the conditions Rc + rc = rm (Rc = 12,000 ohms)
The maximum voltage gain
For the typical junction transistor, RL = 100,000 ohms, Rg = 10 ohms
The maximum voltage gain
Notice that in all of the above cases, the voltage gain is slightly less than unity. This is typical of the grounded collector connection.
|
|
Home  Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors Grounded Emitter and Grounded Collector Transistors  The Grounded Collector Connection The Grounded Collector Connection  Voltage Gain Voltage Gain |
|
Last Update: 2007-09-12



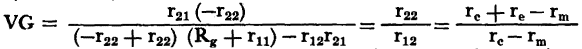

 ;
; and Rg = 10 ohms,
and Rg = 10 ohms,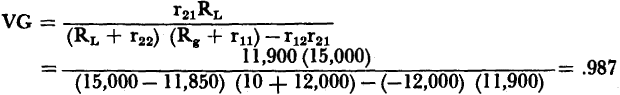
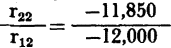 = .985
= .985